Finding the Age of a Page
 One of the more difficult challenges on the Web is determining when a page was created. We simply can not trust the date and time stamps provided with the content we read as both good guys and bad guys alike change the date of their posts as necessary.
One of the more difficult challenges on the Web is determining when a page was created. We simply can not trust the date and time stamps provided with the content we read as both good guys and bad guys alike change the date of their posts as necessary.
Search engines, however, can provide a much better set of statistics than a site’s own timestamps. The only issue is that gleaning the needed information can be difficult. Fortunately, a relatively new Firefox plugin entitled Link Diagnosis helps with that by taking the dirty work out of determining when a page was indexed by Google.
The tool, while not perfect, can be a valuable asset when trying to determine approximately when a page appeared on the Web.
How it Works
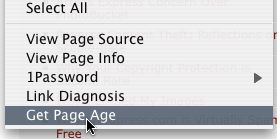 Link Diagnosis is actually a robust plugin designed to analyze incoming links to a URL for SEO purposes. However, as one of its “hidden features” it is able to deteremine, approximately, the day the URL appeared in Google.
Link Diagnosis is actually a robust plugin designed to analyze incoming links to a URL for SEO purposes. However, as one of its “hidden features” it is able to deteremine, approximately, the day the URL appeared in Google.
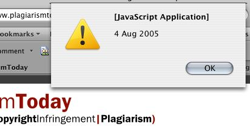
It works simply by having the user right click the page they want to check, select the “Get Page Age” option and, after a few seconds they are greeted with a JavaScript popup containing the date the script detected the site appeared.
It works by using Google’s INURL command which, when used in conjunction with a date filter, causes Google to display a date by each resulting URL. What the plugin does is take the URL you wish to check, create the search query and then automatically extract the applicable date, thus turning a multi-step process into a one-click solutions.
For anyone seeking to find out the date of a site, this could prove to be both a powerful tool and a good time saver as well.
Why to Use It
There are many reasons why you might want to check out the age of a particular page.
For one, you can use it to check if a spam blog or a plagiarist was indexed by Google before or after your original post (provided it was indexed at all). This can help determine what action you should take against the site.
However, many will also find its non-repudiation services to be very useful. If there ever is a dispute about who posted an article or an image first, this tool can help resolve it by providing an independent view on which went up first.
Though certainly not as accurate as Numly or MyFreeCopyright, using Google is far more accurate than looking at the Web Archive, especially considering that the latter can take over six months to display any information about a URL.
Still, Link Diagnosis is still far from perfect in this area. there are many issues one will have if one tries to rely upon this for non-repudiation.
Limitations
 Before you begin to make heavy use of this service bear in mind the following caveats:
Before you begin to make heavy use of this service bear in mind the following caveats:
- Google’s Limitations: The biggest issue of using the INURL method is that Google is not always index a site or a page immediately after it goes up. There are often delays. Also, the service can only work with pages already in the Google database, anything that has been blacklisted, either by the creator or by Google, will return no results.
- URLs and Not Content: The function will tell you when the URL appeared in Google, not the content on the page. For permalinks that may be acceptable but dynamic pages, such as the front page of Plagiarism Today, it can create a problem.
- Different Owners: Also, the system detects when a URL was first indexed by Google, not who owned it at the time. If a site changes ownership, even if it is taken out of Google during the transition, the date shown for the home page will be long to the original owner.
In short, the tools is subject to the exact same gaming and manipulation that Google and the other search engines are. As such, it can provide some quick and dirty information, especially on permalinks, but should never be taken as the ultimate gospel on the age of a page.
Link Diagnosis is no substitute for a true non-repudiation service and it does not claim to be.
Conclusions
Personally, I find the other features of Link Diagnosis much more compelling than its “page age” feature. Though it is great for a quick analysis, especially of a spam blog permalink, it may not always tell the complete truth or have the information you are seeking.
It is a great analysis tool but it should not be assumed to be the plain truth. There are plenty of ways that it could be wrong.
So, as with every tool, be sure to use it in conjunction with common sense and logic. Have it available, use it if needed, but don’t use it as a replacement for your own judgment.
No tool is that powerful.
Want to Reuse or Republish this Content?
If you want to feature this article in your site, classroom or elsewhere, just let us know! We usually grant permission within 24 hours.
